Understanding Home Care Services and Their Role in the USA
Home care services have become an essential component of healthcare delivery across the United States, providing vital support to millions of individuals who prefer to receive care in the comfort of their own homes. These services encompass a wide range of medical and non-medical assistance designed to help people maintain their independence while addressing various health conditions, disabilities, or age-related challenges.

The landscape of home care in America has evolved significantly over the past decades, transforming from basic companion services to comprehensive healthcare solutions that rival traditional institutional care. This shift reflects changing demographics, healthcare preferences, and technological advancements that make home-based care increasingly viable and effective.
An Overview of Home Care Options for Seniors and Individuals
Home care services in the United States fall into two primary categories: skilled medical care and non-medical personal care. Skilled services include nursing care, physical therapy, occupational therapy, and medical social work provided by licensed healthcare professionals. These services typically require physician orders and are often covered by Medicare or private insurance when medically necessary.
Non-medical home care focuses on activities of daily living such as bathing, dressing, meal preparation, medication reminders, and companionship. These services help individuals maintain their quality of life and independence without requiring medical licensure from caregivers. Many families combine both types of care to create comprehensive support systems tailored to specific needs.
How Home Care Supports Health and Daily Living in the United States
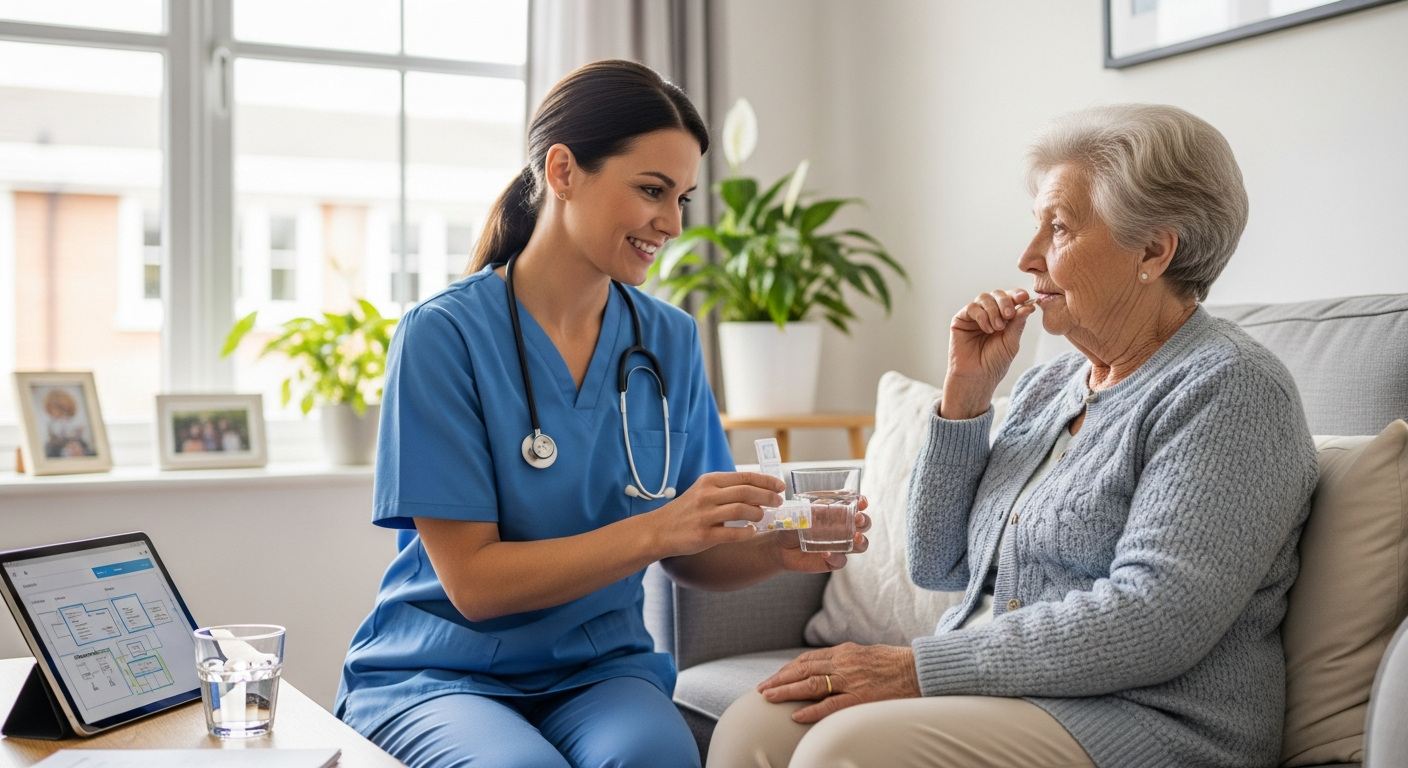
Research consistently demonstrates that home care can improve health outcomes while reducing healthcare costs. Patients receiving care at home often experience faster recovery times, reduced risk of hospital-acquired infections, and improved emotional well-being compared to those in institutional settings. The familiar environment provides psychological comfort that can accelerate healing and maintain cognitive function.
Home care also enables personalized care plans that adapt to individual preferences, cultural backgrounds, and family dynamics. This customization extends to meal preferences, daily routines, and social interactions that institutional care often cannot accommodate. For chronic conditions like diabetes, heart disease, or dementia, consistent home-based monitoring and support can prevent complications and emergency hospitalizations.
Key Considerations When Planning Home Care in the USA
Selecting appropriate home care requires careful evaluation of several factors. Medical needs assessment should involve healthcare providers to determine the level of skilled care required. Family members must also consider the home environment’s safety and accessibility, potentially requiring modifications like grab bars, ramps, or emergency response systems.
Financial planning represents another crucial consideration, as costs vary significantly based on care type, frequency, and geographic location. Families should explore insurance coverage options, including Medicare benefits for skilled care, Medicaid waiver programs for long-term care, and private insurance policies that may cover certain services.
| Provider Type | Services Offered | Cost Estimation |
|---|---|---|
| Visiting Angels | Personal care, companionship, respite care | $20-30 per hour |
| Home Instead | Senior care, Alzheimer’s care, personal care | $22-35 per hour |
| Comfort Keepers | Personal care, companionship, technology support | $18-28 per hour |
| Interim HealthCare | Skilled nursing, therapy, personal care | $25-45 per hour |
| BrightStar Care | Medical and non-medical care, pediatric services | $23-40 per hour |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Trends and Developments in Home Care Services Across the United States
Technology integration represents the most significant trend shaping modern home care. Remote monitoring devices, telehealth platforms, and mobile applications now enable real-time health tracking and virtual consultations with healthcare providers. These innovations improve care coordination while reducing the need for frequent in-person visits.
The aging baby boomer population continues driving demand for home care services, with projections indicating substantial growth through 2030. This demographic shift has prompted increased investment in caregiver training programs, specialized services for conditions like dementia, and innovative care delivery models that combine human caregivers with technological support.
Regulatory changes at both federal and state levels are expanding access to home care services through Medicaid programs and Medicare Advantage plans. These policy developments recognize home care’s cost-effectiveness compared to nursing home placement and its alignment with consumer preferences for aging in place.
Workforce development remains a critical challenge and opportunity within the home care industry. States are implementing training standards, career advancement pathways, and competitive compensation structures to attract and retain qualified caregivers. These efforts aim to ensure service quality while meeting growing demand.
Home care services have established themselves as indispensable components of America’s healthcare system, offering personalized, cost-effective alternatives to institutional care. As the industry continues evolving through technological advancement and policy support, home care will likely play an increasingly central role in supporting individuals’ health and independence throughout their lives.