How connected cars collect and utilize real-time data
The automotive industry is undergoing a revolutionary transformation with the advent of connected cars. These vehicles, equipped with advanced sensors and communication systems, are redefining the driving experience by collecting and utilizing real-time data. This article explores the intricate ways in which connected cars gather information and how this data is leveraged to enhance safety, efficiency, and overall user experience.
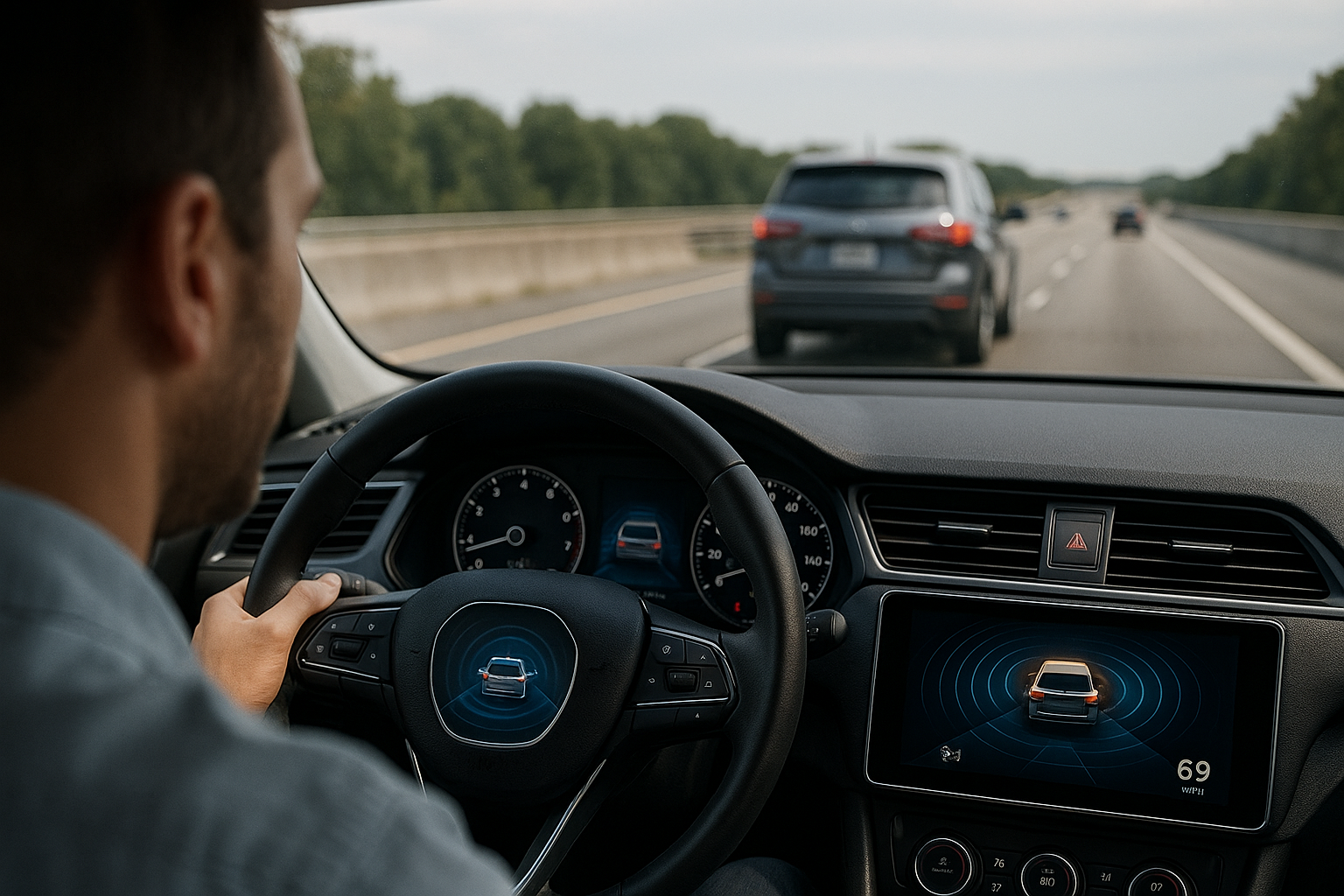

What types of data do connected cars collect?
Connected cars are equipped with a myriad of sensors that continuously gather various types of data. These include GPS location, speed, acceleration, braking patterns, fuel consumption, and engine performance metrics. Additionally, these vehicles collect environmental data such as temperature, humidity, and road conditions. Advanced models even incorporate cameras and radar systems that capture information about surrounding traffic, pedestrians, and potential obstacles.
The onboard diagnostics system (OBD-II) plays a crucial role in collecting data related to the vehicle’s health, including engine RPM, coolant temperature, and battery voltage. This wealth of information forms the foundation for numerous applications and services that make connected cars smarter and more responsive to both driver needs and external conditions.
How is real-time data transmitted and processed?
Connected cars rely on sophisticated communication networks to transmit the collected data in real-time. Most modern vehicles use cellular networks (4G LTE or 5G) to establish a constant connection with cloud servers. Some also utilize Wi-Fi or dedicated short-range communication (DSRC) systems for specific applications.
Once transmitted, the data is processed by powerful cloud computing systems that can analyze vast amounts of information quickly. These systems use advanced algorithms and machine learning techniques to derive meaningful insights from the raw data. The processed information is then used to provide real-time services to the driver, update vehicle systems, or inform broader traffic management solutions.
What are the key applications of real-time data in connected cars?
The utilization of real-time data in connected cars spans a wide range of applications, each designed to enhance different aspects of the driving experience:
-
Predictive Maintenance: By analyzing engine performance data, connected cars can predict potential issues before they become serious problems. This allows for timely maintenance, reducing the likelihood of breakdowns and extending the vehicle’s lifespan.
-
Traffic Management: Real-time location and speed data from multiple connected cars can be aggregated to provide accurate traffic flow information. This helps in optimizing routes, reducing congestion, and improving overall traffic management in urban areas.
-
Safety Enhancements: Data from sensors and cameras can be used to alert drivers to potential hazards, such as sudden braking by vehicles ahead or pedestrians entering the roadway. In more advanced systems, this information can trigger automated emergency braking or steering assistance.
-
Personalized Driving Experience: By analyzing driving patterns and preferences, connected cars can adjust various settings automatically, such as seat position, climate control, and infotainment preferences, to suit individual drivers.
How do connected car platforms integrate with smartphones?
Connected car platforms are increasingly designed to seamlessly integrate with smartphones, creating a unified digital ecosystem for users. This integration typically occurs through dedicated mobile apps that serve as an interface between the vehicle and the user’s smartphone.
Key aspects of this integration include:
-
Remote Access: Users can lock/unlock their cars, start the engine, or control climate settings remotely through their smartphones.
-
Vehicle Health Monitoring: Smartphone apps provide real-time updates on vehicle status, including fuel levels, tire pressure, and maintenance alerts.
-
Navigation and Trip Planning: Routes can be planned on a smartphone and seamlessly transferred to the vehicle’s navigation system.
-
Infotainment Control: Smartphones can be used to control the car’s audio system, select playlists, or access streaming services.
-
Data Synchronization: Personal data such as contacts, calendars, and preferences can be synchronized between the smartphone and the vehicle’s infotainment system.
What are the latest trends in connected infotainment systems?
Connected infotainment systems are evolving rapidly, with several key trends shaping the user experience:
-
Voice Assistants: Advanced natural language processing is enabling more sophisticated voice commands, allowing drivers to control various vehicle functions hands-free.
-
Augmented Reality Displays: Heads-up displays (HUDs) are becoming more advanced, overlaying navigation information and safety alerts directly onto the windshield.
-
Personalized Content Delivery: Infotainment systems are leveraging user data to provide personalized content recommendations, from music to news updates.
-
Over-the-Air Updates: Software updates can be delivered remotely, adding new features and improving system performance without the need for dealership visits.
-
Integration of Third-Party Apps: Car manufacturers are opening up their platforms to third-party developers, allowing for a wider range of apps and services to be integrated into the vehicle’s infotainment system.
What does the future hold for autonomous driving and connected ecosystems?
The future of autonomous driving is intrinsically linked to the development of connected car ecosystems. As vehicles become more connected and data-driven, they pave the way for increasingly sophisticated autonomous capabilities:
-
Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) Communication: Future connected cars will communicate not only with other vehicles but also with infrastructure, pedestrians, and the broader Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystem.
-
Advanced AI and Machine Learning: These technologies will enable cars to make more complex decisions based on real-time data, improving safety and efficiency in autonomous driving scenarios.
-
Seamless Mobility Services: Connected ecosystems will facilitate the integration of various transportation modes, allowing for smooth transitions between autonomous vehicles, public transport, and other mobility solutions.
-
Enhanced Cybersecurity: As cars become more connected, robust cybersecurity measures will be crucial to protect against potential threats and ensure the integrity of autonomous systems.
-
Regulatory Framework Development: The evolution of connected and autonomous vehicles will necessitate new regulatory frameworks to address issues of data privacy, liability, and safety standards.
In conclusion, the collection and utilization of real-time data by connected cars represent a significant leap forward in automotive technology. As these systems continue to evolve, they promise to revolutionize not only how we drive but also how we interact with our vehicles and the broader transportation ecosystem. The future of mobility is undoubtedly connected, data-driven, and increasingly autonomous.